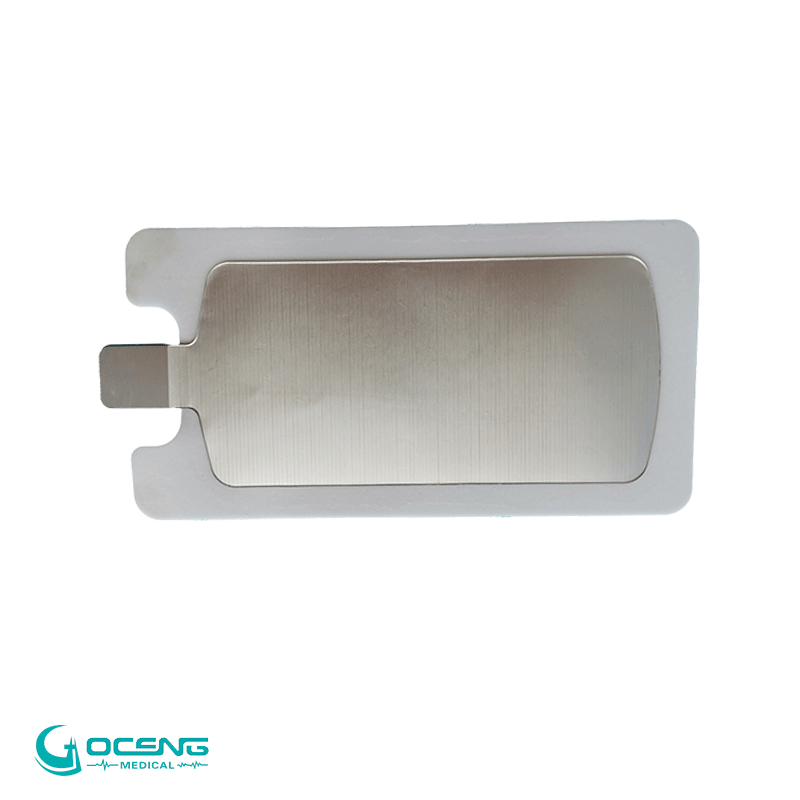
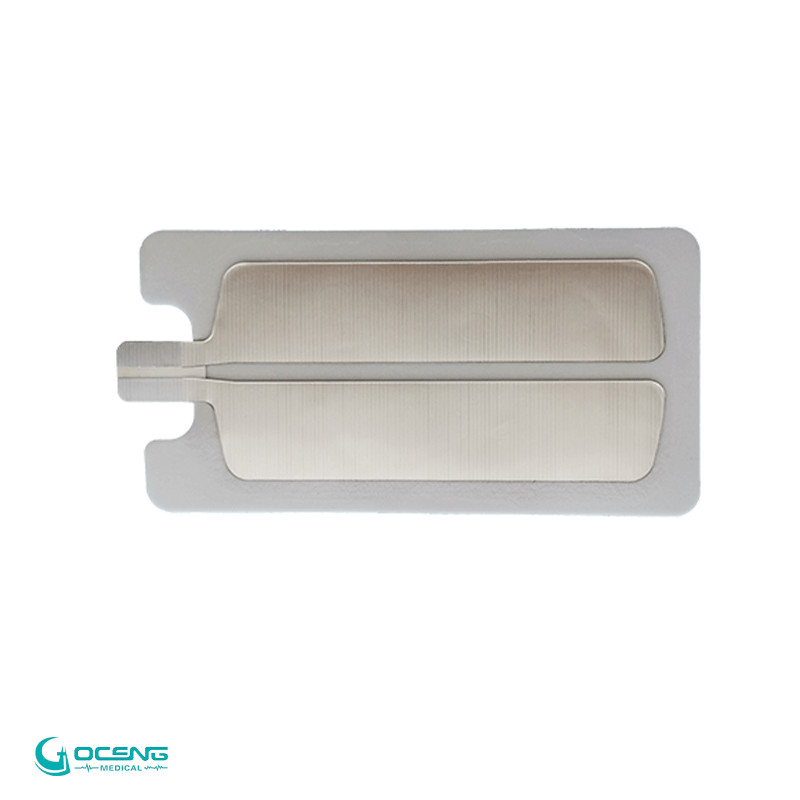
In high-frequency surgical procedures, neutral electrodes play a crucial role in completing the electrical circuit necessary for the application of radiofrequency (RF) energy. High-frequency surgery, also known as electrosurgery, uses high-frequency alternating current (typically in the radiofrequency range) to cut, coagulate, or ablate tissues. The neutral electrode is an essential component in this system.
Here's how the neutral electrode works in high-frequency surgical procedures:
1. Electrosurgical Unit (ESU): The electrosurgical unit is the device that generates the high-frequency electrical current. It consists of a generator, an active electrode (often a handpiece with a cutting or coagulating tip), and a neutral electrode.
2. Application of RF Energy: The surgeon applies the RF energy to the tissue using the active electrode. This high-frequency current induces the desired surgical effects, such as cutting or coagulation, by generating heat in the tissue.
3. Closed Electrical Circuit: For the electrosurgical unit to function properly, there must be a closed electrical circuit. The electrical current flows from the active electrode into the patient's tissues and then back to the generator through the neutral electrode.
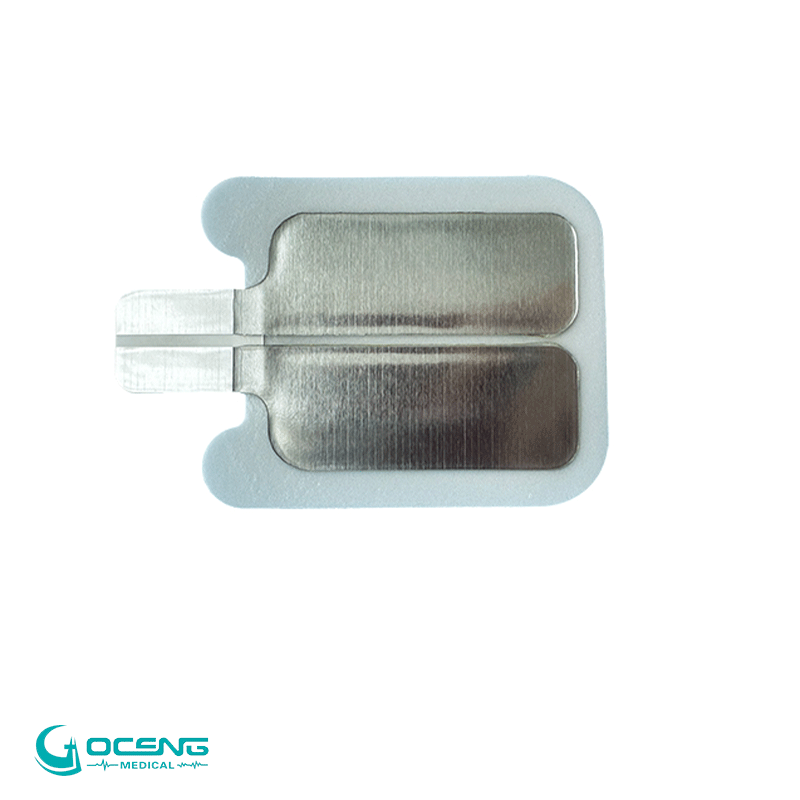
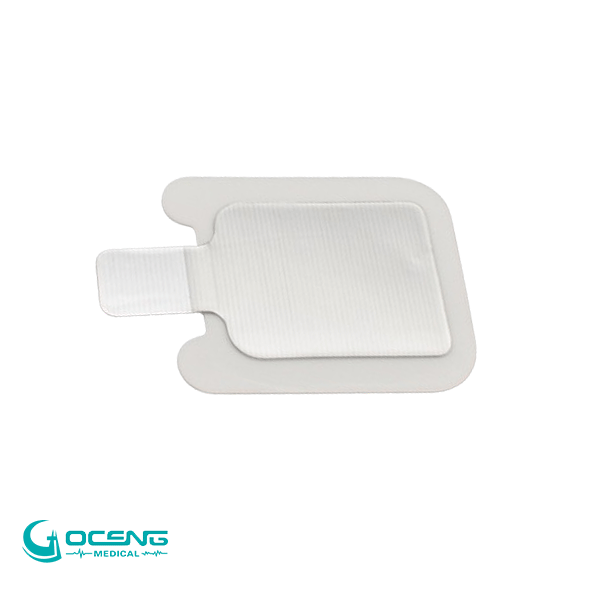
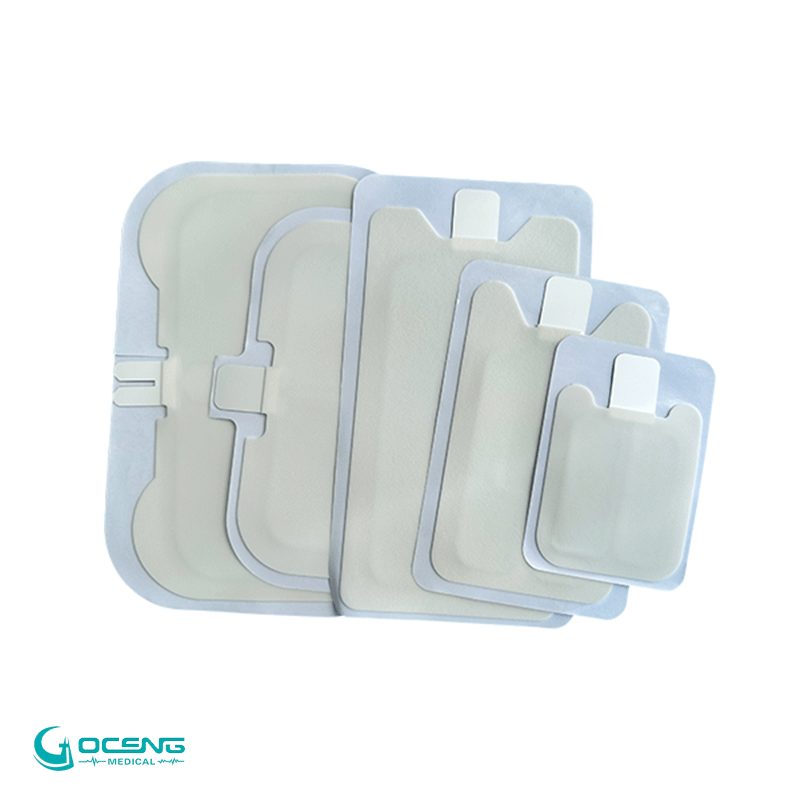
4. Neutral Electrode Placement: The neutral electrode serves as the return path for the electrical current. It is typically a large, conductive pad or plate that is placed on the patient's body, away from the surgical site. This electrode ensures that the electrical current completes the circuit and returns to the generator without causing unintended effects on surrounding tissues.
5. Avoiding Burns and Injuries: Proper placement and adherence of the neutral electrode are crucial to avoid burns or injuries to the patient. The large surface area of the neutral electrode helps disperse the electrical current over a broader area, preventing concentrated heat that could lead to burns.
6. Monitoring Impedance: Some modern electrosurgical units have impedance monitoring systems to continuously monitor the electrical impedance between the active and neutral electrodes. Monitoring impedance helps ensure proper contact and functionality of the neutral electrode, enhancing patient safety.
7. Single-Use Electrodes: In many cases, neutral electrodes are designed for single-use to maintain hygiene standards and prevent the risk of cross-contamination between patients.
It's important for healthcare professionals to follow manufacturer guidelines and best practices when using high-frequency surgical equipment, including proper placement and monitoring of the neutral electrode. This ensures the safety and effectiveness of the electrosurgical procedure. Check more at : www.gocengmed.com