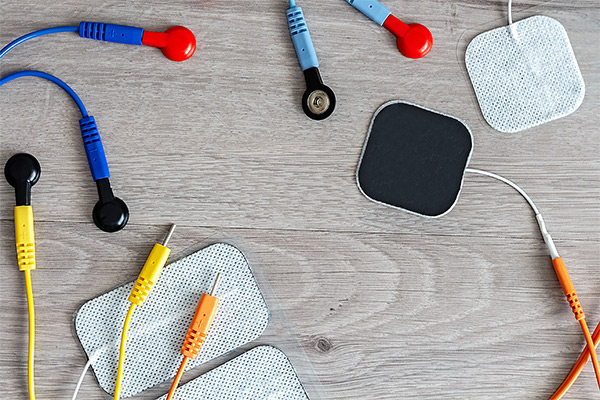
Electrotherapy has long been a staple in the realm of physical rehabilitation and pain management. Central to this therapeutic modality are the electrotherapy electrodes, the conduits that deliver electrical currents to the body's tissues. These electrodes are critical in treatments designed to alleviate pain, improve circulation, and facilitate muscle function. This article delves into the efficacy of electrotherapy electrodes in rehabilitation treatments and their role in modern healthcare.
The Mechanism of Electrotherapy
Electrotherapy works by attaching electrodes to the skin, which then transmit electrical pulses through the surface into deeper lying muscle and tissue. These pulses mimic the action potential coming from the central nervous system, causing the muscles to contract. Depending on the frequency, intensity, and duration of these impulses, various therapeutic benefits can be achieved.
Pain Management
One of the most significant applications of electrotherapy is in pain relief, particularly for patients with chronic musculoskeletal pain. Techniques such as Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS) use electrodes to deliver low-voltage currents, which are thought to interrupt pain signals traveling to the brain. Studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of TENS in conditions like osteoarthritis, fibromyalgia, and after surgical procedures, providing a non-pharmacological pain control option.
Muscle Stimulation and Strength Functional
Electrical Stimulation (FES) is another electrotherapy technique that employs electrodes to enhance motor function in individuals who have experienced strokes, spinal cord injuries, or other conditions that impair muscle performance. By stimulating the appropriate muscle groups, FES can help patients develop muscle strength and endurance, improve joint range of motion, and prevent muscle atrophy.
Tissue Repair and Wound Healing
Electrical stimulation has been shown to accelerate the healing process of tissues, including skin, muscle, and tendons. The electrical currents can enhance blood flow to the injured area, reduce swelling, and promote the release of growth factors that are essential for tissue repair. This is particularly beneficial in the treatment of wounds that are slow to heal, such as diabetic ulcers.
Enhancing Drug Delivery
Iontophoresis is a technique that uses electrotherapy electrodes to facilitate the transdermal delivery of medication. By applying a current, ions of the medicine are driven into the skin, allowing for localized treatment of conditions such as inflammation or calcium deposits. This method of delivery can reduce systemic side effects and provide targeted therapy.
Considerations in Electrotherapy
While electrotherapy has many benefits, it's essential to use it appropriately. The placement of electrodes, the selection of current parameters, and the duration of treatment must be tailored to each individual's needs and conditions. Physical therapists and healthcare providers must assess the patient's medical history, including any contraindications for electrical stimulation, such as the presence of a pacemaker or pregnancy.
Conclusion
Electrotherapy electrodes play a crucial role in rehabilitation and pain management. They offer a versatile and non-invasive means of treatment that can be customized to the needs of each patient. With advancements in technology, the use of electrotherapy continues to expand, offering hope and improved quality of life for patients with various conditions. As research evolves, so too will the applications of electrotherapy, solidifying its place as a cornerstone of rehabilitative care.
Check more at : www.gocengmed.com